PaginaEntry: differenze tra le versioni
Creata pagina con "__NOTOC__ <!-- ✅ AUTORE --> {{ArtBy|Gianni Frisardi}} <!-- ✅ BLOCCO ABSTRACT --> <div class="chapter-content"> <div class="chapter-abstract"> <p><strong>Abstract</strong><br /> The masticatory system, which includes teeth, occlusion, muscles, joints, and the central and peripheral nervous system, is increasingly understood as a complex system rather than a simple biomechanical mechanism. This shift in perspective aligns with Thomas Kuhn's stages of paradigm change..." |
Nessun oggetto della modifica |
||
| Riga 1: | Riga 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<h1>{{PAGENAME}}</h1> | |||
<!-- ✅ AUTORE --> | <!-- ✅ AUTORE --> | ||
{{ArtBy|Gianni Frisardi}} | {{ArtBy|autore=Gianni Frisardi}} | ||
<!-- ✅ BLOCCO ABSTRACT --> | <!-- ✅ BLOCCO ABSTRACT --> | ||
Versione attuale delle 11:15, 11 lug 2025
PaginaEntry
Article by: Gianni Frisardi
|
Abstract
The masticatory system, which includes teeth, occlusion, muscles, joints, and the central and peripheral nervous system, is increasingly understood as a complex system rather than a simple biomechanical mechanism. This shift in perspective aligns with Thomas Kuhn's stages of paradigm changes, where anomalies in traditional models trigger the search for new paradigms. In the context of Masticationpedia, a new interdisciplinary approach to the diagnosis and treatment of malocclusion emerges, focusing on "Occlusal Dysmorphisms" rather than "Malocclusions." Recent advances in electrophysiological tests, such as motor evoked potentials and mandibular reflexes, reveal functional symmetry in the masticatory system, even in patients with occlusal discrepancies. This discovery challenges the traditional understanding of malocclusion, suggesting that neuromuscular dynamics play a crucial role in maintaining masticatory function. Consequently, interdisciplinary diagnoses that consider both occlusal and neuromuscular factors are necessary for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
This paradigm shift has implications for current rehabilitative therapies, including orthodontics and prosthetics, which have traditionally focused on achieving occlusal stability. However, considering the masticatory system as a complex system requires an integrative approach that incorporates both aesthetic and neurophysiological factors to prevent relapses and achieve long-term functional stability. The emerging field of OrthoNeuroGnathodontic treatments exemplifies this interdisciplinary approach, offering innovative strategies to address masticatory disorders.
Viewing the masticatory system through the lens of complexity science, the field of dentistry can expand its understanding of occlusal stability and dysfunction, ultimately leading to new treatment paradigms that improve patient outcomes. This new model does not replace traditional treatments but seeks to enrich them with a broader interdisciplinary perspective, in line with the evolution of masticatory rehabilitation science.
🧾 Page | 💬 Open blog discussion
Ab ovo [1][1]
Latin for 'from the beginning'
Before delving into the analysis of Masticationpedia, we must first introduce some preliminary considerations, particularly regarding two fundamental dimensions—social and scientific-clinical—that characterize both the current era and the one immediately preceding it.
The Phases of Paradigm Change According to Thomas Kuhn
In the last hundred years, technological and methodological innovations [2][2]
🧪 Cross-sectional study analyzing dental innovations over the past 30 years, identifying those that practicing dentists believe have most influenced patient care. 🧬 Thirty experts from the International Association for Dental Research selected the most relevant innovations, which were then surveyed among U.S. dentists who graduated before 1995 and were clinically active for over 50% of the time. 🧩 The most cited innovations were adhesive materials (74.5%), dental implants (71.9%), direct bonding (71.2%), magnifying lenses (54.7%), universal infection control precautions (48.6%), and digital imaging (46.0%), with differences between generalists and specialists: oral surgeons and periodontists (OMSPER) also favored CBCT (74%) and regenerative techniques (68%). The general consensus highlights the importance of implants, imaging, lenses, and universal precautions; generalists value adhesive materials and bonding, while specialists cite CBCT and tissue engineering. 📌 The study concludes that innovations with direct clinical impact are perceived as the most decisive, suggesting that future research should also consider cost-effectiveness and patient perception. have exponentially increased, even in dentistry. These developments have had a significant impact on clinical decision-making, schools of thought, and the fundamental principles of the discipline, with the explicit goal of improving quality of life. A notable example is the vision proposed in "Exposure Science in the 21st Century"[3][3]
The document Exposure Science in the 21st Century: A Vision and a Strategy (2012) by the National Academy of Sciences proposes a renewed vision of exposure science, aiming to address emerging challenges for human and environmental health. 🧠 What is exposure science? Exposure science studies the contact between humans or other organisms and environmental agents (chemical, physical, or biological), analyzing the duration, intensity, and effects of such exposures. This discipline is crucial for understanding how environmental stressors affect health and for developing prevention and mitigation strategies. 🌐 The proposed vision: the “eco-exposome” The concept of “eco-exposome” extends exposure science from the point of contact between stressor and receptor within the organism to the surrounding environment, including the ecosphere. 🔬 Technological innovations and strategic collaborations: The document highlights technological advancements, such as advanced environmental sensors, analytical methods, molecular technologies, and computational tools, which offer new opportunities to collect more accurate and comprehensive data on exposures. 🛠️ Implementing the vision: To realize this vision, it is necessary to: Develop standardized and non-targeted methods to collect information on exposures. 🎯 Long-term goals: The ultimate goal is to use exposure science to: Quickly assess and mitigate exposures to emerging threats. 📌 In summary, the document proposes a transformation of exposure science, moving from an approach focused on individual stressors to an integrated and holistic vision, to address the environmental and health challenges of the 21st century.
However, this accelerated growth is not without conceptual side effects. Some of these effects may be ambiguous, if not outright contrary to apparent progress, generating clinical and scientific paradoxes.[4][4]
Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) have ushered in a new era of targeted therapies, particularly in the fields of immunotherapy and oncology. MAbs have evolved from murine antibodies to fully human antibodies, with significant improvements in immunogenicity and safety. However, the safety of these agents is of particular concern, with reports of side effects associated with their use. These side effects have shaken the confidence of many researchers in MAbs. 🧠 This review comprehensively summarizes the side effects of MAbs in clinical use, highlighting the prevention and management of adverse reactions. Although many MAbs are well tolerated, and new MAbs are continuously being developed, it is difficult to guarantee that every new formulation is completely safe. The clinical use of MAbs will face increasing challenges in the future. Physicians should be vigilant about potentially lethal side effects and treat them as soon as possible.
Such ambiguities, instead of weakening the entire epistemological structure, are a symptom of a mature system capable of recognizing its own limits and seeking a paradigm evolution, as described by Thomas Kuhn in his famous theory on the development of science.
Kuhn's Phases in Dentistry
Thomas Kuhn identifies five distinct phases in the evolution of a scientific paradigm. In Masticationpedia, we will focus on the three most relevant ones, which best fit the evolution of masticatory rehabilitation science.
|
|
|
Epistemology
Epistemology (from the Greek ἐπιστήμη, epistēmē, “certain knowledge” or “science”, and λόγος, logos, “discourse”) is the branch of philosophy that studies the necessary conditions for acquiring scientific knowledge and the methods through which it is achieved.[5][5]
The term was coined by the Scottish philosopher James Frederick Ferrier, in his Institutes of Metaphysic (1854); see Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy, James Frederick Ferrier (1808—1864)
In particular, epistemology analyzes the foundations, validity, and limits of scientific knowledge. In English-speaking countries, the term "epistemology" is often used as a synonym for the theory of knowledge or gnoseology.
The central problem of epistemology, today as in the time of Hume,[6][6]
📌 David Hume, son of lawyer Joseph Home of Chirnside and Katherine Falconer, daughter of the president of the College of Justice, was born the third child in a mansion on the north side of the Lawnmarket in Edinburgh. Although of noble origins, his family was not very wealthy, and he was entrusted with a small portion of their estate. He changed his surname from Home to Hume in 1734 to better maintain the Scottish pronunciation even in England.[7][7]
📌 Scientific knowledge should be verifiable. Replications promote verifiability in several ways. Most directly, replications can confirm empirical claims. Replication research also promotes the dissemination of information necessary for other aspects of verification; creates meta-scientific knowledge about which results to consider credible even in the absence of replications; and reinforces a broader norm that scientists should check each other's work. is the issue of verifiability.
According to Hempel's paradox, every example that does not contradict a theory confirms it. This is expressed in propositional logic as:
![]() Consider the following statement: ✅ “If a person has TMD, then they experience orofacial pain.” We can represent this in logic as , where: 🎯 represents "The person has TMD." 🎯 represents "The person experiences orofacial pain." In this case, "If a person has TMD, then they experience orofacial pain" is equivalent to saying “either the person does not have TMD (), or they experience orofacial pain ().” 🧠 The formula is true in the following cases: If the person does not have TMD (), the statement is true regardless of orofacial pain. If the person has TMD () and experiences orofacial pain (), the statement is true. The statement is false only if the person has TMD () but does not experience orofacial pain (), contradicting the implication condition.
Consider the following statement: ✅ “If a person has TMD, then they experience orofacial pain.” We can represent this in logic as , where: 🎯 represents "The person has TMD." 🎯 represents "The person experiences orofacial pain." In this case, "If a person has TMD, then they experience orofacial pain" is equivalent to saying “either the person does not have TMD (), or they experience orofacial pain ().” 🧠 The formula is true in the following cases: If the person does not have TMD (), the statement is true regardless of orofacial pain. If the person has TMD () and experiences orofacial pain (), the statement is true. The statement is false only if the person has TMD () but does not experience orofacial pain (), contradicting the implication condition.
But no theory can be definitively confirmed: an infinite number of future experiments could always refute it.[8][8]
📌 A fundamental issue in the theory of statistical inference concerns how one should measure statistical evidence. Certainly, terms like “statistical evidence” or simply “evidence” are widely used in statistical contexts. However, it is fair to say that a precise characterization of this concept remains somewhat elusive. Our goal here is to provide a definition of how to measure statistical evidence in relation to a specific statistical problem. Since evidence is what causes belief change, it is proposed to measure evidence based on the extent of belief change, from the prior to the posterior moment. 🧠 Consequently, our definition implies the existence of pre-existing beliefs, which raises questions about subjectivity and objectivity in statistical analyses. This aspect is addressed through a principle that requires the falsifiability of every element involved in the statistical analysis. These considerations lead to the need to verify any conflicts between prior beliefs and observed data, and to measure the prior bias present in an initial distribution
|
But it's not all that obvious... |
P-value
In medicine, we often rely on statistical inference to validate experimental results. One of the most well-known tools is the 'P-value', or probability value, an indicator used in significance testing. ![]() The P-value represents the probability that the observed results are due to chance, assuming the null hypothesis is true. It should not be used as a binary criterion (e.g., ) for scientific decisions, as values close to the threshold require additional verification, such as cross-validation. P-hacking (repeating tests to achieve significance) increases false positives. Rigorous experimental designs and transparency about all tests conducted can mitigate this risk. Type I error increases with multiple tests: for independent tests at threshold , the Family-Wise Error Rate (FWER) is . The Bonferroni correction divides the threshold by , , but can increase false negatives. The Benjamini-Hochberg False Discovery Rate (FDR) allows more discoveries with an acceptable proportion of false positives. The Bayesian approach uses prior knowledge to balance prior and data with a posterior distribution, offering a valid alternative to the P-value. To combine P-values from multiple studies, meta-analysis uses methods like Fisher's: . 🧠 In summary, the P-value remains useful if contextualized and integrated with other measures, such as confidence intervals and Bayesian approaches.
The P-value represents the probability that the observed results are due to chance, assuming the null hypothesis is true. It should not be used as a binary criterion (e.g., ) for scientific decisions, as values close to the threshold require additional verification, such as cross-validation. P-hacking (repeating tests to achieve significance) increases false positives. Rigorous experimental designs and transparency about all tests conducted can mitigate this risk. Type I error increases with multiple tests: for independent tests at threshold , the Family-Wise Error Rate (FWER) is . The Bonferroni correction divides the threshold by , , but can increase false negatives. The Benjamini-Hochberg False Discovery Rate (FDR) allows more discoveries with an acceptable proportion of false positives. The Bayesian approach uses prior knowledge to balance prior and data with a posterior distribution, offering a valid alternative to the P-value. To combine P-values from multiple studies, meta-analysis uses methods like Fisher's: . 🧠 In summary, the P-value remains useful if contextualized and integrated with other measures, such as confidence intervals and Bayesian approaches.
However, even the P-value, for years a fundamental criterion in evidence-based medicine, is now undergoing profound revision. In 2019, a campaign published in "Nature", signed by over 800 scientists, questioned the rigid use of statistical significance.[9][9]
📌 In the March edition of Nature, over 800 scientists signed a commentary calling for the retirement of the term “statistical significance” [1]. The main arguments of the authors concern the fact that the scientific literature is full of erroneous and potentially harmful interpretations of associations based on an arbitrary and binary classification, founded on a p-value of 0.05. The authors illustrate the critical issues of this approach, providing concrete examples where it has led to erroneous conclusions within and between different studies. 🧠 Additionally, analyzing 791 articles published in five academic journals, they found that 51% of them misinterpreted a statistically non-significant result as an indication of the absence of an effect. This "silent revolution" in the field of statistical inference promotes a more reflective, contextual, and scientifically honest approach. Among the most authoritative voices in this debate are:
- Rodgers JL – who speaks of a “silent methodological revolution”[10][10]
📌 In recent decades, a silent methodological revolution has occurred almost without discussion: a revolution in modeling. In contrast, the 20th century ended with lively debates about the utility of null hypothesis significance testing (NHST). However, this controversy may have been at least partly irrelevant, as the modeling revolution has rendered the NHST debate superfluous in various ways. I begin by presenting a history of NHST and modeling, and the relationships between the two. Next, I define and illustrate the principles guiding the development and evaluation of mathematical models. This is followed by a discussion on the difference between using statistical procedures in a rule-based framework and constructing mathematical models within a scientific epistemology. 🧠 In postgraduate psychology education, almost exclusive attention is given to the first, rule-based approach. The pedagogical implications of this imbalance and the need for revised teaching to account for the modeling revolution are then described. Finally, the discussion turns to how focusing on modeling leads to an evolution of statistical practice in more progressive directions. The epistemological basis of statistics has shifted: from a set of mechanically applied procedures to the construction and evaluation of statistical and scientific models.
- Meehl P – who suggests replacing significance tests with 'confidence intervals' and 'verifiable numerical predictions'[11][11]
📌 Significance tests have a role in social science research, but their widespread use in theory evaluation is often harmful. The cause of this does not lie in the mathematics itself, but in the poor understanding, by social scientists, of the logical relationship between theory and facts, i.e., a lack of methodological or epistemological clarity.🧭 Theories imply observations, but the reverse is not true. Although a theory's success in deriving a fact tends to corroborate it, this confirmation is weak unless the fact has a very low a priori probability and there are few plausible alternative theories. 🧭 Detecting a non-zero difference or correlation — as occurs when rejecting the null hypothesis — generally does not have a very low a priori probability, because in social sciences practically everything is correlated with everything else, regardless of the theory. 🎯 In the "strong" use of significance tests, the theory predicts a precise numerical value, or a very narrow range, so the test poses a serious risk of falsification if the theory were objectively incorrect. In general, it is preferable to construct a confidence interval, which provides richer information and still implies the null hypothesis's refutation if a difference falls outside the interval. 🧠 Significance tests are usually more justifiable in technological contexts (e.g., evaluating an intervention) rather than in theory evaluation. It would be useful to have a quantitative index measuring how accurately a theory predicts a risky fact, and an example of such an index is proposed. Unlike current widespread practices, textbooks and statistics courses should clarify and emphasize the significant semantic (logical) gap separating a substantive (causal, compositional) theory from a statistical hypothesis.
- Sprenger & Hartmann – proponents of the 'Bayesian philosophy of science'[12][12]
📌 How should we reason in science? Jan Sprenger and Stephan Hartmann offer an innovative view on classic themes in the philosophy of science, using a single key concept to explain and clarify numerous aspects of scientific reasoning. 🧭 They propose that good arguments and good inferences are characterized by their effect on our rational degrees of belief. 🧠 Contrary to the view that there is no room for subjective attitudes in "objective science," Sprenger and Hartmann explain the value of compelling evidence through a cycle of variations on the theme of representing rational degrees of belief through subjective probabilities (and their modification through Bayesian conditioning). In this way, they integrate Bayesian inference — the main theory of rationality in the social sciences — with the scientific practice of the 21st century. Bayesian Philosophy of Science thus shows how modeling such attitudes improves our understanding of causes, explanations, confirmatory evidence, and scientific models in general. Their approach combines a scientifically oriented and mathematically refined perspective with conceptual analysis and a particular focus on the methodological problems of modern science, especially in statistical inference, making it a valuable resource for both philosophers and practitioners of science.
The 'American Statistical Association' has supported this change by publishing a special issue of the journal 'The American Statistician', titled “Statistical Inference in the 21st Century: A World Beyond p < 0.05”.[13][13]
🧠 Some of you, exploring this special issue of The American Statistician, might wonder if it is a lecture from pedantic statisticians intent on moralizing about what not to do with p-values, without offering real solutions to the difficult problem of separating signal from noise in data and making decisions under uncertainty. Fear not. In this issue, thanks to 43 innovative and stimulating articles written by forward-thinking statisticians, the help we need arrives. The volume proposes new ways of representing uncertainty and invites us to move beyond the dependence on the P-value as the sole metric of scientific truth.
Interdisciplinarity
A superficial view might suggest a conflict between the disciplinary rigidity of the 'Physical Paradigm of Science' ![]() The "Physical Paradigm of Science" describes a prevailing epistemological approach in the physical sciences, centered on deterministic models and rigorous experimental methodologies. This paradigm relies on empirical observations and the scientific method to seek universal laws governing natural phenomena.Key Characteristics1. Determinism: Assumes that natural phenomena follow fixed laws, allowing accurate predictions based on initial conditions. 2. Measurability and Reproducibility: Emphasizes quantitative measurements and reproducible experiments to confirm results in different contexts. 3. Isolation of Variables: Focuses on analyzing specific effects by isolating variables, often idealizing systems under controlled conditions. While effective in classical natural sciences, the physical paradigm has limitations in complex fields like neurophysiology, where dynamic interactions and variability challenge deterministic models. Application in Masticatory Neurophysiology: In masticatory neurophysiology, the physical paradigm helps develop basic models but fails to explain emergent behaviors, such as motor unit recruitment in response to complex stimuli. Towards an Integrated Paradigm: Emerging is an "Engineering Paradigm of Science," offering a more adaptive approach that considers complexity, allowing more flexible predictive models that account for non-linear interactions in biological systems and the systemic openness of the Engineering Paradigm of Science
The "Physical Paradigm of Science" describes a prevailing epistemological approach in the physical sciences, centered on deterministic models and rigorous experimental methodologies. This paradigm relies on empirical observations and the scientific method to seek universal laws governing natural phenomena.Key Characteristics1. Determinism: Assumes that natural phenomena follow fixed laws, allowing accurate predictions based on initial conditions. 2. Measurability and Reproducibility: Emphasizes quantitative measurements and reproducible experiments to confirm results in different contexts. 3. Isolation of Variables: Focuses on analyzing specific effects by isolating variables, often idealizing systems under controlled conditions. While effective in classical natural sciences, the physical paradigm has limitations in complex fields like neurophysiology, where dynamic interactions and variability challenge deterministic models. Application in Masticatory Neurophysiology: In masticatory neurophysiology, the physical paradigm helps develop basic models but fails to explain emergent behaviors, such as motor unit recruitment in response to complex stimuli. Towards an Integrated Paradigm: Emerging is an "Engineering Paradigm of Science," offering a more adaptive approach that considers complexity, allowing more flexible predictive models that account for non-linear interactions in biological systems and the systemic openness of the Engineering Paradigm of Science ![]() The Engineering Paradigm of Science emphasizes practical applications, interdisciplinary collaboration, and understanding complex systems. It contrasts with traditional deterministic models, focusing instead on solving real-world problems, particularly in fields like biology, medicine, and social sciences.Key Characteristics Problem-Solving Orientation: Prioritizes solutions to complex issues over purely theoretical models. Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Encourages integrating knowledge from various disciplines, enhancing understanding through shared experiences. Focus on Complex Systems: Recognizes emergent behavior and the interconnectedness of system components, acknowledging that outcomes can be unpredictable and non-linear. Iterative Process: Embraces an adaptive approach, refining models based on empirical data and feedback to improve responsiveness.Technological Integration: Applies engineering principles to enhance research design and data analysis, utilizing simulations and computational modeling. Application in Masticatory Neurophysiology In masticatory neurophysiology, this paradigm promotes innovative diagnostic tools and therapeutic approaches. By integrating neurophysiology, biomechanics, and materials science, it provides a comprehensive view of jaw function and dysfunction. The Engineering Paradigm of Science fosters collaboration and innovation, ultimately leading to advances that improve our understanding of complex systems and enhance practical outcomes in various fields.
The Engineering Paradigm of Science emphasizes practical applications, interdisciplinary collaboration, and understanding complex systems. It contrasts with traditional deterministic models, focusing instead on solving real-world problems, particularly in fields like biology, medicine, and social sciences.Key Characteristics Problem-Solving Orientation: Prioritizes solutions to complex issues over purely theoretical models. Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Encourages integrating knowledge from various disciplines, enhancing understanding through shared experiences. Focus on Complex Systems: Recognizes emergent behavior and the interconnectedness of system components, acknowledging that outcomes can be unpredictable and non-linear. Iterative Process: Embraces an adaptive approach, refining models based on empirical data and feedback to improve responsiveness.Technological Integration: Applies engineering principles to enhance research design and data analysis, utilizing simulations and computational modeling. Application in Masticatory Neurophysiology In masticatory neurophysiology, this paradigm promotes innovative diagnostic tools and therapeutic approaches. By integrating neurophysiology, biomechanics, and materials science, it provides a comprehensive view of jaw function and dysfunction. The Engineering Paradigm of Science fosters collaboration and innovation, ultimately leading to advances that improve our understanding of complex systems and enhance practical outcomes in various fields.
📘 According to an important European study,[14][14]
📌 In scientific policies, it is generally recognized that problem-solving based on science requires interdisciplinary research. 📌 However, the epistemological processes leading to effective interdisciplinary research are still poorly understood. 🧭 This article aims to outline an epistemology of interdisciplinary research (IDR), particularly for solving "real-world" problems. The focus is on why researchers encounter cognitive and epistemic difficulties in conducting interdisciplinary activities. Based on a study of educational literature, it is concluded that higher education lacks clear ideas about the epistemology of interdisciplinary research and, consequently, how to teach it. It is hypothesized that the lack of philosophical attention to the epistemology of IDR is due to the predominance of a philosophical paradigm of science, defined as the "physical paradigm of science," which hinders the recognition of the deep epistemological challenges of interdisciplinarity both in the philosophy of science and in scientific education and research.🧠 An alternative philosophical paradigm, defined as the "engineering paradigm of science," is therefore proposed, which involves different assumptions regarding aspects such as the purpose of science, the nature of knowledge, the epistemic and pragmatic criteria for accepting knowledge, and the role of technological tools. According to this engineering paradigm, the production of knowledge for epistemic purposes becomes the goal of science, and "knowledge" (theories, models, laws, concepts) is interpreted as an epistemic tool useful for performing cognitive tasks by epistemic agents, rather than as an objective representation of aspects of the world independent of the way it is constructed. This implies that knowledge is inevitably shaped by the way it is constructed. Moreover, the way different scientific disciplines construct knowledge is guided by the specificities of the discipline itself, analyzable through disciplinary perspectives. 🧠 It follows that knowledge and its epistemic uses cannot be understood without at least some understanding of how it is constructed. Consequently, scientific researchers need so-called "metacognitive scaffolding" to assist them in analyzing and reconstructing the processes of knowledge construction and the differences between disciplines. In the engineering paradigm, these metacognitive scaffolding are also interpreted as epistemic tools, but in this case, tools that guide, enable, and limit the analysis and articulation of knowledge production processes (i.e., explain the epistemological aspects of doing research). In interdisciplinary research, such metacognitive scaffolding assist interdisciplinary communication, with the aim of analyzing and articulating how each discipline constructs its own knowledge.
- interdisciplinarity requires:
- metacognitive tools ("cognitive scaffolds")
- common languages between different disciplines
- flexible epistemological models
Another study proposes an engineering interpretation of knowledge[15][15]
📌 To address the complexity of biological systems and attempt to generate applicable results, current biomedical sciences are adopting concepts and methods from engineering sciences. Philosophers of science have interpreted this phenomenon as the emergence of an engineering paradigm, particularly in systems biology and synthetic biology. This article aims to articulate the presumed engineering paradigm in contrast to the physical paradigm that supported the rise of biochemistry and molecular biology. This articulation starts from Kuhn's notion of "disciplinary matrix," which indicates what constitutes a paradigm. It is argued that the core of the physical paradigm lies in its metaphysical and ontological assumptions, while the core of the engineering paradigm consists of the epistemic goal of producing knowledge useful for solving problems external to scientific practice. 🧠 Therefore, the two paradigms imply distinct notions of knowledge. While the physical paradigm involves a representational notion of knowledge, the engineering paradigm implies the notion of "knowledge as an epistemic tool". in biomedical contexts: here, knowledge is considered 'an active tool' for solving complex clinical problems, rather than a mere theoretical representation of reality.
🌐 Towards Paradigmatic Innovation
The intersection of these two paradigms not only enriches the scientific method but produces 'Paradigmatic Innovations', which are true epistemological leaps.
🧬As noted by Yegane Guven (2017) [16][16]
📌 In recent years, dentistry has experienced an explosion of scientific and technological innovations that are profoundly transforming both clinical practice and university education; virtual reality, nanotechnology, tissue engineering, personalized medicine, and stem cells are opening new frontiers for diagnosis and treatments, while education integrates biosciences, bioinformatics, and ICT, focusing on research, problem-solving, and experiential approaches; among the most promising innovations: biomimetics, salivary tests, tissue regeneration, and genetic therapies, with the goal of shifting dentistry towards a regenerative and predictive model; accreditation and updating of curricula remain fundamental for training that keeps pace with the times in her review on digital medicine and dentistry. Innovation often arises from:
- biological and digital revolutions
- interdisciplinary contaminations
- systemic rather than reductionist vision
These changes are not incremental but 'paradigmatic', in the sense that they alter the entire way we think, observe, and treat clinical systems, as much as the masticatory function.
Dental Malocclusion
"Malocclusion" derives from the Latin 'malum' (bad) and 'occludere' (to close), literally meaning "incorrect closure" of the teeth.[17][17]
📌 Considered the father of modern orthodontics, Angle defined the first classification system for malocclusions (Class I, Class II, etc.), which is still used today to describe the alignment and relationship of teeth; he simplified the design of orthodontic appliances, founded the first school of orthodontics, the American Association of Orthodontists (later AAO), and the first orthodontic journal, and authored the fundamental work "Treatment of Malocclusion of the Teeth" (1887). Although intuitive, the term “malocclusion” implies a value judgment (“bad”) that is not always supported by functional clinical evidence.
🧪 A PubMed search for the word "malocclusion" yields over 33,000 articles.[18][18]
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=%22malocclusion%22 However, searching for “interdisciplinary diagnosis of malocclusion” reduces the results to 245 articles.[19][19]
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=interdisciplinary+diagnostics+of+malocclusions If 'Differential Diagnosis' is added to this request, the result drops to only 5 articles.[20][20]
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=interdisciplinary+diagnostics+of+malocclusions+AND+differential+diagnosis
|
These data suggest that the concept of "malocclusion" has been overused without adequate functional investigation. |
📌 A study by Smaglyuk et al. emphasizes the need for an interdisciplinary diagnostic approach, especially in children.[21][21]
📌 Introduction: The main task of modern orthodontics is to create a balanced and morphologically stable occlusion, in harmony with facial aesthetics and functional adaptation. 🧭 The purpose of the study is to investigate the relationship between dento-facial anomalies and somatic pathologies. Patients and methods: Materials and methods: A bibliographic study was conducted using the Medline and Google Scholar databases. 🧭 Review: The human body is a biological system consisting of interconnected and subordinate elements. Any anomaly in the functioning of this system can cause a functional alteration in a single organ. This principle fully applies to dento-facial anomalies and deformities, whose development is closely related to other pathologies. 🧠 The diagnosis, therapeutic strategy, and prevention of dento-facial anomalies and deformities should be considered in the context of the integrity of the not yet fully formed child's body, recognizing the interdependence between the form and functions of its organs and systems.
📊 Towards "Occlusal Dysmorphisms"
📎 In Masticationpedia, the term "Occlusal Dysmorphisms" is preferred because:
- not all asymmetrical occlusions are pathological
- masticatory function can be preserved even in the presence of asymmetries
- there are neuromuscular adaptations that compensate for discrepancies
👉 This leads to a reflection: 'is it correct to treat all malocclusions?' Not always.
Clinical Case
In the following case, the patient presents:
- unilateral posterior crossbite
- anterior open bite
The patient would be a candidate for:
- orthodontic treatment
- orthognathic surgery
However, the patient 'refuses therapy' citing normal masticatory function. The dentist explains the long-term risks but respects the decision.
|
What does this case tell us? |
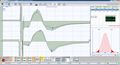
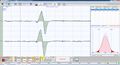
📌 That function can prevail over form. To understand this, electrophysiological tests were performed:
🎯 The results show organic-functional symmetry 'despite the visual malocclusion', suggesting that neuromuscular function can compensate for morphological discrepancies.
Occlusal Dysmorphisms and not Malocclusion... which, as we will see shortly, is a completely different topic.
Discussion
The consideration of the masticatory system as a complex system is further validated in light of recent developments in neurophysiology applied to dental occlusion. Studies conducted on animal models, particularly Sprague-Dawley rats, have shown that even minimal occlusal modifications (e.g., trimming of the mandibular incisor) can induce significant changes in the primary motor cortex of the face (face-M1), with evident manifestations of functional and structural neuroplasticity[22][22]
. 🧠 The modification of dental occlusion can influence oral sensorimotor functions, and not all patients can adapt to restorative treatments. By studying Sprague-Dawley rats, neuroplasticity of the facial primary motor cortex (face-M1) was observed in response to repeated trimming of the mandibular incisors, followed by the restoration of occlusal contacts. The changes, mapped with intracortical microstimulation (ICMS), showed significant differences between cerebral hemispheres in the latency and distribution of motor areas of the tongue and mandible. These results suggest that face-M1 neuroplasticity could be an adaptive mechanism to respond to alterations in dental occlusion.
These cortical modifications include, for example, the variation in tongue activation latency between cerebral hemispheres, the variation in the number of cortical activation sites for the tongue and mandible, and the modification of the depth of the center of gravity of the involved cortical areas. These results suggest that the loss and subsequent restoration of occlusal contacts can alter orofacial motor representations, paving the way for new interpretative models of masticatory function based on adaptive neuroplasticity.
Similarly, it emerges that both the primary somatosensory cortex (face-SI) and the motor cortex (face-MI) play a central role in orofacial sensorimotor integration, participating not only in the initiation and control of voluntary movements (e.g., mandibular opening) but also in semi-automatic movements such as chewing and swallowing [23][23]
🧠 The facial somatosensory and motor cortex regulates automatic and voluntary orofacial movements. Their neuroplasticity allows adaptation or lack thereof to oral changes (such as occlusal alterations or prostheses), influencing the recovery of sensorimotor functions and quality of life, especially in patients with neurological disorders or orofacial pain.
These two cortical areas, although distinct in function, are deeply interconnected: face-MI continuously receives input from face-SI, and together they form the so-called “face sensorimotor cortex”[24][24]
🧠 This article provides an overview of the neural mechanisms involved in the somatosensory and motor functions of the face and mouth and, to a lesser extent, the pharynx and larynx. The focus is particularly on the neural basis of touch, temperature, and orofacial pain, with special emphasis on pain, as it is common in the skin, teeth, muscles, joints, and other tissues of the orofacial region and can cause long-term suffering through various painful states or syndromes. Particular attention is also given to the neural processes that regulate the numerous reflexes and other motor functions of the orofacial area, particularly those related to chewing, swallowing, and associated neuromuscular functions. Only a few details are dedicated to other important functions of the face and mouth, such as smell, taste, and speech. Their integrated activity is mediated by complex central circuits, which include corticobulbar projections directed to the motor nuclei of the cranial nerves (primarily the trigeminal nucleus), responsible for mandibular muscle activation.
The range and complexity of orofacial movements require sophisticated neural circuitries that provide for the coordination and control of these movements and their integration with other motor patterns such as those associated with breathing and walking. This chapter is dedicated to Jim Lund whose many research studies have made major contributions to our knowledge of the role of brainstem and cerebral cortex in orofacial motor control. Our own investigations using intracortical microstimulation (ICMS), cortical cold block, and single neuron recordings have documented that the face primary motor area (MI) and primary somatosensory area (SI) are involved in the control not only of elemental and learned orofacial movements but also of the so-called semiautomatic movements such as mastication and swallowing, the control of which have been largely attributed in the past to brainstem mechanisms. Recent studies have also documented that neuroplasticity of the face sensorimotor cortex is a feature of humans and animals trained in a novel oral motor behavior, and that it reflects dynamic and adaptive events that can be modeled by behaviorally significant experiences, including pain and other alterations to the oral environment. Furthermore, our findings of the disruptive effects of the face sensorimotor cortex cold block indicate that the face MI and SI are also critical in the successful performance of an orofacial motor skill once it is learned. Future studies aimed at the further demonstration of such changes and at their underlying mechanisms and their sequence of appearance in the face sensorimotor cortex and associated cortical areas represent crucial steps for understanding the intracortical processes underlying neuroplasticity related to oral motor learning and adaptation. In view of the role that cortical neuronal ensembles play in motor execution, learning, and adaptation (Nicolelis and Lebedev, 2009), these studies should include the properties and plasticity of neuronal ensembles in several related cortical areas in addition to a specific focus on single neurones or efferent microzones within the face MI or SI. As recently noted (Martin, 2009; Sessle et al., 2007, 2009), such research approaches are also important for developing improved rehabilitative strategies to exploit these mechanisms in humans suffering from chronic orofacial pain or sensorimotor disorders.
In summary, trigeminal neuroplasticity emerges as the key to understanding adaptation (or lack thereof) to occlusal modifications. It must guide both diagnosis and therapeutic strategies, inspiring truly personalized rehabilitation protocols. OrthoNeuroGnathodontic treatments and beyond, being based on this systemic vision, represent the most advanced and coherent clinical model to address the challenges of modern dentistry.In light of these data, it is evident that alterations in craniofacial and occlusal morphology—traditionally interpreted through static biomechanical models—must instead be understood from a dynamic functional perspective. The clinical evaluation of the patient cannot therefore disregard an integration of morphology, function, and neurophysiological response. Not every "malocclusion" requires treatment, just as not every "ideal occlusion" guarantees functional well-being.
Conclusion
.🔁 Before concluding, it is essential to clarify that the 'masticatory system' cannot be considered merely as a simple biomechanical mechanism without connecting it to a neurophysiological control system that essentially determines a 'Complex System'. [26][26]
📌 A complex system is a dynamic multi-component system, composed of various subsystems that typically interact with each other in an interdependent manner, analytically describable through mathematical models. This type of system is studied within the field of complexity theory. A global approach is typically necessary, as it is not possible to analytically resolve all components with their interactions, while it is useful to rely on complex computer simulations to evaluate/analyze the dynamic behavior of each component as well as their mutual interactions, which can be described in a simple or linear manner or non-linear (see dynamic system). Typical of complex systems are the concepts of self-organization and emergent behavior. The assumption of a complex system thus embraces most real physical systems with many components, compared to systems considered "simple," more typical of classical physics.
🧩 This implies that elements such as:
- dental occlusion
- temporomandibular joint
- periodontal receptors
- neuromuscular spindles
- central trigeminal nervous system
do not act in isolation, segmenting the biological system into biomechanical and neurophysiological but in 'synergy', producing an "Emergent Behavior". ![]() The **masseter silent period** (MSP) is a relevant example of emergent behavior in masticatory neurophysiology. This reflex is activated by sudden blows to the chin, leading to a brief cessation of electrical activity in the masseter muscle, and is closely related to the recruitment of motor units. During MSP, there is a specific modulation of motor unit recruitment, regulated by the central nervous system, to respond to external stimuli. In the context of emergent behavior, this reflex is not limited to a single muscle but represents a coordinated response involving synergies between various neuronal centers and antagonist muscles. Mathematically, we can describe the probability of an emergent response as a function of the input variables that influence the activation of motor units: where represents the non-linear interaction between incoming stimuli (such as the type and intensity of the blow to the chin) and the central integration processes of the trigeminal system. This model helps to understand how MSP reflects an integrated and adaptive response that emerges from complex neurophysiological circuits rather than from a single neural pathway.
The **masseter silent period** (MSP) is a relevant example of emergent behavior in masticatory neurophysiology. This reflex is activated by sudden blows to the chin, leading to a brief cessation of electrical activity in the masseter muscle, and is closely related to the recruitment of motor units. During MSP, there is a specific modulation of motor unit recruitment, regulated by the central nervous system, to respond to external stimuli. In the context of emergent behavior, this reflex is not limited to a single muscle but represents a coordinated response involving synergies between various neuronal centers and antagonist muscles. Mathematically, we can describe the probability of an emergent response as a function of the input variables that influence the activation of motor units: where represents the non-linear interaction between incoming stimuli (such as the type and intensity of the blow to the chin) and the central integration processes of the trigeminal system. This model helps to understand how MSP reflects an integrated and adaptive response that emerges from complex neurophysiological circuits rather than from a single neural pathway.
📚 An important conceptual synthesis is represented by the work of 'Kazem Sadegh-Zadeh', "Handbook of Analytic Philosophy of Medicine", which describes medicine as a systemic science.[27][27]
📌 Medical practice is practiced morality and clinical research belongs to normative ethics. This book clarifies and develops this thesis: 1. analyzing the structure of medical language, knowledge, and theories; 2. investigating the foundations of the clinical encounter; 3. introducing the logic and methodology of clinical decision-making; 4. suggesting comprehensive theories on organism, life, and psyche; on health, disease, and pathology; on etiology, diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, and therapy; and 5. investigating the central moral and metaphysical issues in medical practice and research.
🧠 The elements of the masticatory system are consistent with the activity of the central trigeminal nervous system, as evidenced in electrophysiological tests. This reinforces the idea that "Malocclusion" is an 'insufficient heuristic category': the correct term is "Occlusal Dysmorphism".
🏁 In this context, 'OrthoNeuroGnathodontic' treatments emerge as paradigmatic: they integrate aesthetics, function, and neurosciences to achieve:
- occlusal stability
- prevention of relapses
- functional resilience
📖 Recent studies confirm the importance of post-therapy stability:[28][28]
📌 Comparing the post-surgical skeletal stability between counterclockwise rotation (CCWR) of the maxillomandibular complex (MMC) and clockwise rotation (CWR) of the MMC for the correction of dentofacial deformities. Materials and methods: To achieve the study's purpose, we designed and implemented a systematic review with meta-analysis based on PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines. A search strategy was developed and a search was conducted in major databases – PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) – to find all relevant articles published from the beginning until March 2016. Inclusion criteria were randomized controlled clinical trials, controlled clinical trials, retrospective studies, and case series, with the aim of comparing the post-surgical stability of CCWR and CWR of the MMC. 🧪 The analysis was performed using lateral cephalometric analysis of mean post-operative values and the correlation between surgical and post-operative changes in the occlusal plane angle and linear changes in points A and B. A weighted mean difference analysis was performed using a random-effects model with 95% confidence intervals. Results: A total of 133 patients were enrolled from 3 studies (CCWR, n = 83; CWR, n = 50). 🧪 All included studies had a moderate risk of bias. 🧠 There was a statistically significant difference between CCWR and CWR of the MMC in post-operative changes in the occlusal plane angle (P = 0.034), but no statistically significant difference was found in the correlation between surgical and post-operative changes in the occlusal plane angle in the 2 groups. No statistically significant difference was found between CCWR and CWR of the MMC regarding stability between immediate post-surgical and longest follow-up evaluations, concerning vertical and horizontal positions at points A and B (P > 0.05). Conclusion: CCWR, compared to CWR, for the correction of dentofacial deformities in the absence of pre-existing temporomandibular joint pathologies, is skeletally stable concerning post-surgical changes in the occlusal plane, as well as vertical and horizontal changes in the maxilla and mandible[29][29]
📌 The stability of bilateral sagittal split osteotomy (BSSO) is an important goal for every surgeon. The article examines the factors influencing the stability of the surgical outcome. Particular emphasis is given to the different types of fixation of bone fragments. Their advantages and disadvantages in clinical use are discussed. 🧠 Recurrence after BSSO is generally classified as early and long-term. Early recurrence is usually caused by movements at the osteotomy site or failure of the temporomandibular joint and should be defined as surgical dislocation. Long-term recurrence occurs due to progressive condylar resorption of the temporomandibular joint, causing a loss of condylar and mandibular ramus height. Four different types of fixation in orthognathic surgery have been described: rigid intermaxillary fixation, osteosuture, osteosynthesis, and fixation with biodegradable materials.
What do we mean by “Complex Systems” when we talk about masticatory functions?
📌 Epistemological Premise: Language Before Complex Systems
In particular, the epistemic structure of medical language presents deep conceptual ambiguities: concepts such as disease, normality, function and adaptation are often assumed to be invariant, despite being historically and culturally determined.Even before addressing the definition of complex systems in medicine, it is necessary to reconsider the way we use and interpret medical language, both on the semantic and formal levels.
As Kazem Sadegh-Zadeh emphasizes in his monumental work Handbook of Analytic Philosophy of Medicine, the language of medicine is intrinsically fuzzy: many of its definitions operate on gradual and non-binary categories, where semantic imprecision is not a limitation, but a structural component of clinical knowledge.[30][30]
🧠 Medical practice is practiced morality and clinical research belongs to normative ethics. This book clarifies and develops this thesis: 1. analyzing the structure of medical language, knowledge, and theories; 2. investigating the foundations of the clinical encounter; 3. introducing the logic and methodology of clinical decision-making; 4. suggesting comprehensive theories on organism, life, and psyche; on health, disease, and pathology; on etiology, diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, and therapy; and 5. investigating the central moral and metaphysical issues in medical practice and research.
Similarly, Eric Cassell has shown that the concept of disease cannot be reduced to either a biological dysfunction or a mere statistical deviation: it is rather the result of a semantic negotiation between patient, clinician, and cultural context.[31][31]
🧠 The issue of suffering and its relationship to organic diseases has rarely been addressed in the medical literature. This article offers a description of the nature and causes of suffering in patients undergoing medical treatment. A distinction is made, based on clinical observations, between suffering and physical discomfort. Suffering is experienced by people, not just bodies, and originates from challenges that threaten the integrity of the person as a complex social and psychological entity. Suffering can include physical pain, but it is not limited to it. The relief of suffering and the cure of disease must be considered as two complementary duties of a medical profession truly dedicated to the care of the sick. The inability of physicians to understand the nature of suffering can lead to medical intervention that (although technically adequate) not only fails to relieve suffering but becomes itself a source of suffering.
Finally, the biopsychosocial model of George Engel proposes to interpret every clinical event within a multi-level network of meanings—biological, psychological, social, and semantic—anticipating that systemic and complex vision that is now at the center of contemporary medicine.[32][32]
The dominant model of disease today is biomedical, and it leaves no room within tis framework for the social, psychological, and behavioral dimensions of illness. A biopsychosocial model is proposed that provides a blueprint for research, a framework for teaching, and a design for action in the real world of health care.>/Small>
- ↑ Latin for 'from the beginning'
- ↑ Heft MW, Fox CH, Duncan RP, «Assessing the Translation of Research and Innovation into Dental Practice», in JDR Clin Trans Res, 2019».
DOI:10.1177/2380084419879391 - ↑ «Exposure Science in the 21st Century. A Vision and a Strategy», National Research Council, Division on Earth and Life Studies, 2012».
ISBN: 0-309-26468-5 - ↑ Liu L, Li Y, «The unexpected side effects and safety of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies», in Drugs Today, 2014, Barcelona».
DOI:10.1358/dot.2014.50.1.2076506 - ↑ The term was coined by the Scottish philosopher James Frederick Ferrier, in his Institutes of Metaphysic (1854); see Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy, James Frederick Ferrier (1808—1864)
- ↑ David Hume (1711–1776) was a Scottish philosopher.
- ↑ Srivastava S, «Verifiability is a core principle of science», in Behav Brain Sci, Cambridge University Press, 2018».
DOI:10.1017/S0140525X18000869 - ↑ Evans M, «Measuring statistical evidence using relative belief», in Comput Struct Biotechnol J, 2016».
DOI:10.1016/j.csbj.2015.12.001 - ↑ Amrhein V, Greenland S, McShane B, «Scientists rise up against statistical significance», in Nature, 2019».
DOI:10.1038/d41586-019-00857-9 - ↑ Rodgers JL, «The epistemology of mathematical and statistical modeling: a quiet methodological revolution», in Am Psychol, 2010».
DOI:10.1037/a0018326 - ↑ Meehl P, «The problem is epistemology, not statistics: replace significance tests by confidence intervals and quantify accuracy of risky numerical predictions», 1997».
- ↑ Sprenger J, Hartmann S, «Bayesian Philosophy of Science. Variations on a Theme by the Reverend Thomas Bayes», Oxford University Press, 2019».
- ↑ Wasserstein RL, Schirm AL, Lazar NA, «Moving to a World Beyond p < 0.05», in Am Stat, 2019».
DOI:10.1080/00031305.2019.1583913 - ↑ Boon M, Van Baalen S, «Epistemology for interdisciplinary research – shifting philosophical paradigms of science», in Eur J Philos Sci, 2019».
DOI:10.1007/s13194-018-0242-4 - ↑ Boon M, «An engineering paradigm in the biomedical sciences: Knowledge as epistemic tool», in Prog Biophys Mol Biol, 2017».
DOI:10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.04.001 - ↑ Guven Y, «Scientific basis of dentistry», in J Istanb Univ Fac Den, 2017».
DOI:10.17096/jiufd.04646 - ↑ https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Edward_Angle
- ↑ Pubmed, Malocclusion
- ↑ Pubmed, Interdisciplinary diagnosis of malocclusions
- ↑ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=interdisciplinary+diagnostics+of+malocclusions+AND+differential+diagnosis
- ↑ Smaglyuk LV, Voronkova HV, Karasiunok AY, Liakhovska AV, Solovei KO, «Interdisciplinary approach to diagnostics of malocclusions (review)», in Wiad Lek, 2019».
- ↑ Avivi-Arber L, Lee JC, Sessle BJ. Motor cortex neuroplasticity associated with dental occlusion. J Dent Res. 2015;94(12):1751–9. doi:10.1177/0022034515596345
- ↑ Avivi-Arber L, Martin R, Lee JC, Sessle BJ. The Face Sensorimotor Cortex and its Neuroplasticity in Health and Disease. J Dent Res. 2019;98(11):1184–94. doi:10.1177/0022034519865385
- ↑ Iwata K, Sessle BJ. Neural Basis of Orofacial Functions in Health and Disease. J Dent Res. 2019;98(11):1185–1195. doi:10.1177/0022034519865372
- ↑ Review Prog Brain Res. 2011:188:71-82. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53825-3.00010-3. Chapter 5--face sensorimotor cortex: its role and neuroplasticity in the control of orofacial movements. Barry J Sessle , PMID: 21333803 DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-444-53825-3.00010-3
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Complex_system
- ↑ Sadegh-Zadeh Kazem, «[https: //link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-94-007-2260-6 Handbook of Analytic Philosophy of Medicine]», Springer, 2012».
ISBN: 978-94-007-2259-0 - ↑ Essam Ahmed Al-Moraissi, Larry M Wolford.Is Counterclockwise Rotation of the Maxillomandibular Complex Stable Compared With Clockwise Rotation in the Correction of Dentofacial Deformities? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016 Oct;74(10):2066.e1-12. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2016.06.001
- ↑ J Hoffmannová et al.Factors influencing the stability of sagittal split ramus osteotomy. Prague Med Rep. 2008;109(4):286–97.
- ↑ Sadegh-Zadeh Kazem, «[https: //link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-94-007-2260-6 Handbook of Analytic Philosophy of Medicine]», Springer, 2012».
ISBN: 978-94-007-2259-0 - ↑ Cassell EJ. "The Nature of Suffering and the Goals of Medicine." The New England Journal of Medicine, 1982. doi:10.1056/NEJM198203183061204.
- ↑ Engel GL. "The need for a new medical model: a challenge for biomedicine." Science, 1977;196(4286):129–136. doi:10.1126/science.847460.